|
|
|

|
|
| Expression statement | block {} Statement | Branch Statements | Loop Statements | Type Declaration | Variable Declaration | Synchronize Statements | With Statement | Using Statement | Type Alias | Branches are conditional or unconditinal
|
bool switchOk = false;
switch(42)
{
case 1, 2, 3: // test for 1 or 2 or 3
break;
case .toString().equals("41"): // calls 42.toString().equals("41")
switchOk = false;
break;
case >= 41: // calls 42 >= 41
switchOk = true;
break;
default:
switchOk = false;
break;
}
|
 csf_tests_acdk_cfgscript_2_statements_70_Switch_Test_csf.
csf_tests_acdk_cfgscript_2_statements_70_Switch_Test_csf. UnconditionalBranchStatement
UnconditionalBranchStatement
UnconditionalBranchStatement :ReturnStatement |
BreakStatement |
ContinueStatement |
GotoStatement |
ThrowStatement |
TryCatchStatement ;
 ReturnStatement
ReturnStatement
ReturnStatement : 'return' [Expression ] ';'
 BreakStatement
BreakStatement
BreakStatement : 'break' ';'
See also:
 Loop Statements.
Loop Statements. ContinueStatement
ContinueStatement
ContinueStatement : 'continue' ';'
See also:
 Loop Statements.
Loop Statements. GotoStatement
GotoStatement
goto is not implemented. ThrowStatement
ThrowStatement
ThrowStatement : 'throw'The throw statement throws an exception.Expression ';' ;
Exception can be caught by the try catch statement.
Because the implementation of exceptions in CfgScript uses native C++ exceptions, it is possible to catch exceptions thrown in C++ in CfgScript and vice versa.
Sample:
try {
StringArray sa = new StringArray(0);
String s = sa[1];
} catch (acdk.lang.IndexOutOfBoundsException ex) {
out.println(ex.getMessage());
}
|
 Debugging.
Debugging. TryCatchStatement
TryCatchStatement
TryCatchStatement
: 'try' Statement ( 'catch' '(' TypeName VarName ')' Statement )* [ 'finally' Statement ]
;
The try catch statement works the same way like in Java.
Different to C++ and Java the
catch will be tested in the same order
as they declared:
try {
throw new RuntimeError("asdf");
} catch (Throwable ex) {
// this catch branch will be executed
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
// never reach here
}
|
The
try block and independed if the exception was handled
by a catch block.
try {
} catch (RuntimeException ex) {
} finally {
// this code block will be executed independ if inside try block an exception
// was thrown or the the exception was handled in a catch block
}
|
If an exception should be re-thrown in a catch Exception block
throw ex; should
be used (throw; doesn't work).
 Branch Statements
Branch Statements
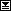 BranchStatement
BranchStatement